When calling a function, you can specify optional named parameters using paramName: value. For example:
enableFlags(bold: true, hidden: false);
When defining a function, use {param1, param2, …} to specify named parameters:
void enableFlags({bool bold, bool hidden}) {...}
Wrapping a set of function parameters in [] marks them as optional positional parameters:
String say(String from, String msg, [String device]) {
var result = '$from says $msg';
if (device != null) {
result = '$result with a $device';
}
return result;
}
Here’s an example of calling this function without the optional parameter:
assert(say('Bob', 'Howdy') == 'Bob says Howdy');
if the parameter is required, add @required annotation in front of the parameter, otherwise everything will be optional
theme in MaterialApp object
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
theme: ThemeData(primarySwatch: Colors.deepOrange),
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text("Easy App Flutter"),
),
body: ProductManager("Food Tester"),
),
);
}
}
RaisedButton(
color: Theme.of(context).primaryColor,
onPressed: () {
setState(() {
_products.add('Advance Food Test');
});
},
child: Text("Add Location")
deepOrange theme with button based on context theme:
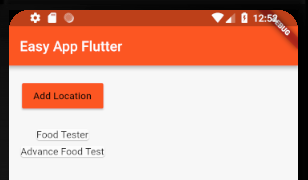
Here parameters in Text(),add() and ProductManager() are positional parameters.
primarySwatch is a named parameters.
Const and Final
final is a reference which cannot reassign value to the variable, but the object is still mutable.
const is not only a immutable reference but also immutable for the value.
final List<String> products = [];
products.add("new"); //this can work.
final List<String> prices = const [];
prices.add("100"); //cannot work.